 This is an image I produced in Excel. It depicts two graphs; y = e^x, and y = e^-x. These two functions are important because they are used in my formula for velocity of the trash in the air.(See my previous post.) The first function, at x = 0, is equal to 1. As x increases, the function grows exponentially, because it is an exponent. The second function, since it is reciprocal, although starting with the same value of 1 at x = 0, decreases exponentially and by the time x reaches 3, for example, the value of the function falls approximately tenfold. This means that the value of the multiplicand in parentheses(basic formula of this experiment) will grow quickly.
This is an image I produced in Excel. It depicts two graphs; y = e^x, and y = e^-x. These two functions are important because they are used in my formula for velocity of the trash in the air.(See my previous post.) The first function, at x = 0, is equal to 1. As x increases, the function grows exponentially, because it is an exponent. The second function, since it is reciprocal, although starting with the same value of 1 at x = 0, decreases exponentially and by the time x reaches 3, for example, the value of the function falls approximately tenfold. This means that the value of the multiplicand in parentheses(basic formula of this experiment) will grow quickly.
Thursday, March 20, 2008
Theoretical Review Part 5: The Exponential Function
 This is an image I produced in Excel. It depicts two graphs; y = e^x, and y = e^-x. These two functions are important because they are used in my formula for velocity of the trash in the air.(See my previous post.) The first function, at x = 0, is equal to 1. As x increases, the function grows exponentially, because it is an exponent. The second function, since it is reciprocal, although starting with the same value of 1 at x = 0, decreases exponentially and by the time x reaches 3, for example, the value of the function falls approximately tenfold. This means that the value of the multiplicand in parentheses(basic formula of this experiment) will grow quickly.
This is an image I produced in Excel. It depicts two graphs; y = e^x, and y = e^-x. These two functions are important because they are used in my formula for velocity of the trash in the air.(See my previous post.) The first function, at x = 0, is equal to 1. As x increases, the function grows exponentially, because it is an exponent. The second function, since it is reciprocal, although starting with the same value of 1 at x = 0, decreases exponentially and by the time x reaches 3, for example, the value of the function falls approximately tenfold. This means that the value of the multiplicand in parentheses(basic formula of this experiment) will grow quickly.
Tuesday, March 18, 2008
Theoretical Review Part 4: Analysis of Trash Velocity
Therefore, at the drop time, velocity will be zero, which is consistent with my experiment. When time becomes very large, mg/b will be multiplied by one minus the reciprocal of e to the power of a large number, with 0 as its limit. Therefore the multiplicand in the parentheses will be one, and therefore the velocity will be constant, and equal to mg/b. Since it is constant at large t, it is terminal velocity. This is also consistent.
Sunday, March 9, 2008
Theoretical Review Part 3: Air Resistance

where m is the mass of the object, b is a constant dependent on the object's cross-sectional area and viscosity of the fluid.
In this project we will try to estimate the constant b from our experiments as an intermediary result.
 I will calculate a number of curves for a number of values of the b-constant. They are shown as curves on the above plot. The lower the curve, the bigger the cross-sectional area of the object. I, then, will drop the object from two floors: 15 and 7. These two drops will give me two times: t7 and t15. Knowing the distance between the seventh and fifteenth floor, I will find the curve on the above graph that describes the movement of the trash. This will be done by finding the curve the area under which between t7 and t15 is equal to the distance between the seventh and fifteenth floors. Knowing the curve will supply the absolute height of a given floor, as well as the value of the b-constant. From the latter, I will be able to estimate the viscosity of the fluid, using the following formula:
I will calculate a number of curves for a number of values of the b-constant. They are shown as curves on the above plot. The lower the curve, the bigger the cross-sectional area of the object. I, then, will drop the object from two floors: 15 and 7. These two drops will give me two times: t7 and t15. Knowing the distance between the seventh and fifteenth floor, I will find the curve on the above graph that describes the movement of the trash. This will be done by finding the curve the area under which between t7 and t15 is equal to the distance between the seventh and fifteenth floors. Knowing the curve will supply the absolute height of a given floor, as well as the value of the b-constant. From the latter, I will be able to estimate the viscosity of the fluid, using the following formula: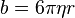
Theoretical Review Part 2
g = 9.8m/s2 (1)

Since the area of a rectangle is height times length, which are measured velocity and measured time, the traveled distance is the area of the shaded rectangle.
The movement of an object with a constant acceleration would look like this:
Using the formula for area of a triangle, we can determine that the distance is half of the measured time(base) times the measured velocity(height):
d = 1/2*t1*v1 (3)
Substituting (2) into (3), we get that distance is half of measured time multiplied by acceleration due to gravity multiplied by measured time:
d = 1/2*t1*g*t1
d = 1/2*g*t1^2 (4)
Using this formula, we can determine the height of the building by measuring the time.
To increase accuracy, we must also take into account air resistance and speed of sound.
Note. From formula (4) it follows that the measurement of the height of the building is linearly dependent on acceleration due to gravity. On time, however, it is quadratically dependant. This means that it is more important to know exact time than exact acceleration.
Theoretical Review Part 1
The factors to be taken into account (in prioritized order) are acceleration/velocity due to gravity, air resistance that the trash is under influence of in the conduit, and speed of sound.
Speed of sound is taken into account to extract time needed for the sound signal to travel up the chute to the drop point.
Project Plan
Experiment
Experiment Analysis
Repeat Experiment(With New Parameters)
Final Conclusions
Science Fair Presentation
Science Fair
